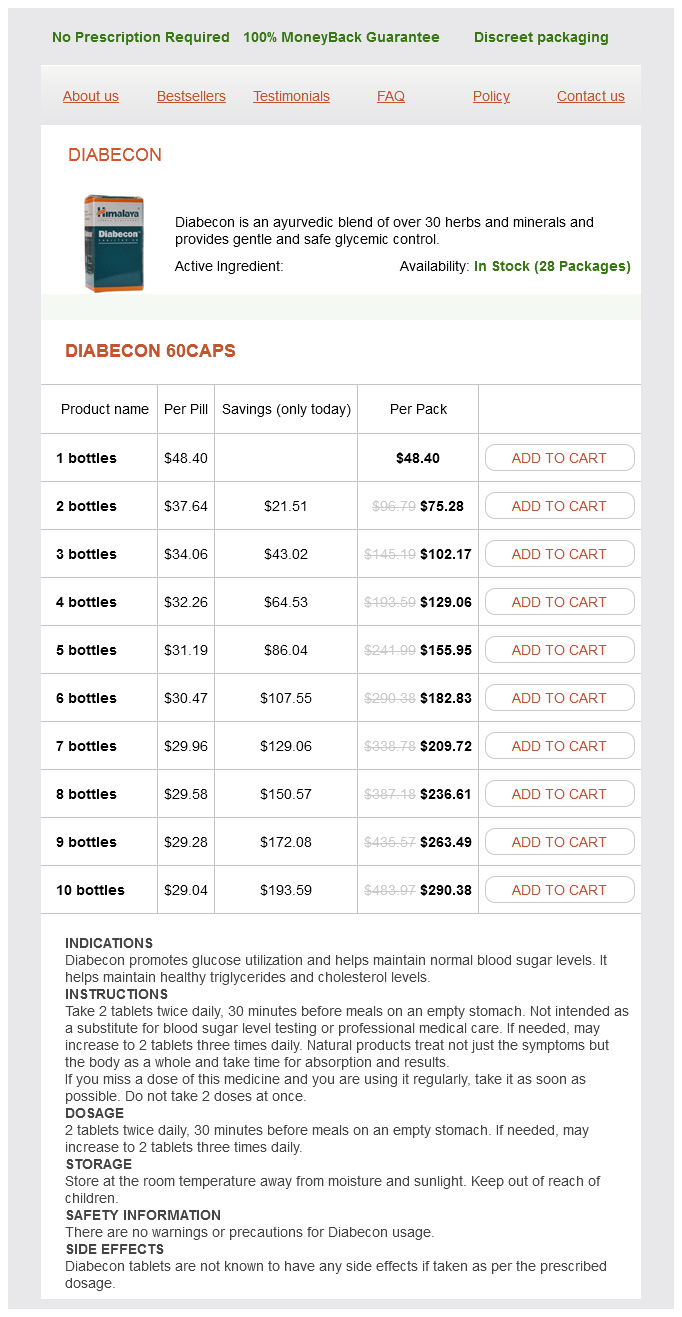
Diabecon 60caps
- 1 bottles - $48.40
- 2 bottles - $75.28
- 3 bottles - $102.17
- 4 bottles - $129.06
- 5 bottles - $155.95
- 6 bottles - $182.83
- 7 bottles - $209.72
- 8 bottles - $236.61
- 9 bottles - $263.49
- 10 bottles - $290.38
Diabecon dosages: 60 caps
Diabecon packs: 1 bottles, 2 bottles, 3 bottles, 4 bottles, 5 bottles, 6 bottles, 7 bottles, 8 bottles, 9 bottles, 10 bottles
In stock: 515
Only $30.85 per item
Description
Secretion of bile salts is the major osmotic force for the generation of bile flow diabetes diagnostic test purchase diabecon 60 caps on-line. The bulk of the bile salt pool is maintained in the gallbladder, followed by the liver, the small intestine, and the extrahepatic bile ducts. As a result, 60% to 70% of the bile acid pool consists of cholic acid and its metabolite deoxycholic acid, with chenodeoxycholic acid occurring less commonly in human bile (Holm et al, 2013; Kullak-Ublick et al, 2004). In the space of Disse within the liver, bile salt uptake into the hepatocytes is very efficient. The sodium-dependent pathway accounts for more than 80% of taurocholate uptake but less than 50% of cholate uptake (Meier & Stieger, 2002). Two mechanisms may be responsible for bile acid transcellular movement: One involves transfer of bile acids from the basolateral membrane to the canalicular membrane via bile acidbinding proteins (Crawford, 1996); the other moves cellular bile salts through vesicular transport. In contrast, the transport of bile salts across the canalicular membrane of hepatocytes represents the rate-limiting step in the overall secretion of bile salts from the blood into bile. Bile salt concentrations are 1000-fold greater within the canaliculi than in the hepatocytes. Chapter 8 Bile secretion and pathophysiology of biliary tract obstruction 125 2013). Recent studies suggest that bile acids are signaling molecules that regulate lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism (Li & Chang, 2015). Phospholipids and cholesterol are formed primarily from lowdensity lipoproteins circulating in plasma and from de novo synthesis by hepatocytes. Less is known about the secretion of biliary lipids compared with bile salt secretion; however, biliary lipid secretion is crucial for cholesterol disposal, intestinal absorption of dietary lipids, and cytoprotection against bile acidinduced hepatocyte and cholangiocyte injury (Arrese & Accatino, 2002). Phospholipid secretion involves the delivery of phospholipids to the inner leaflet of the canalicular plasma membrane (Elferink & Groen, 2000). These patients have no phosphatidylcholine in bile and therefore do not form mixed micelles with bile salts. As a result, toxic bile salts injure the biliary epithelium, resulting in neonatal cholestasis, cholestasis of pregnancy, and cirrhosis in adults. Cholesterol is highly nonpolar and insoluble in water; thus it is insoluble in bile. The key to maintaining cholesterol in solution is the formation of micelles, a bile saltphospholipidcholesterol complex. Bile salts are amphipathic compounds that contain both a hydrophilic and hydrophobic portion. In aqueous solutions, bile salts are oriented with the hydrophilic portion outward. Phospholipids are incorporated into the micellar structure, allowing cholesterol to be added to the hydrophobic central portion of the micelle. Concentration of bile leads to net transfer of phospholipids and cholesterol from vesicles to micelles.
Bissy Nut (Cola Nut). Diabecon.
- How does Cola Nut work?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Cola Nut?
- Weight loss, depression, exhaustion, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), dysentery, diarrhea, anorexia, migraines, mental and physical fatigue, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Cola Nut.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96900
The assistant surgeon displaces the second portion medially and forward diabetes mellitus care plan order diabecon 60 caps on line, and the peritoneum is incised posteriorly along the curved lateral margin of the duodenum. Access is provided to the avascular space between the posterior aspect of the head of the pancreas anteriorly and the perinephric fat and inferior vena cava posteriorly; elevation of the structures should reach the left margin of the inferior vena cava. Duodenotomy Duodenotomy is performed in the lateral duodenal wall by surgical diathermy. It is important to expose and mobilize the third portion of the duodenum to easily identify and operate on the papilla and allow facile closure of the duodenotomy. If the papilla is not easily seen, it can often be palpated as a small elevation in the medial duodenal wall. If the papilla is still not easily seen, a small Nélaton catheter is introduced through the cystic duct stump until it is seen to protrude from the papillary orifice. The forefinger, introduced through the duodenotomy, detects the papilla as a small, thick elevation. The duodenotomy is performed above the junction of the second and third portions of the duodenum; the surgeon takes into account that the papilla usually is located at the junction of the upper two thirds and lower third of the second part of the duodenum. The duodenal incision may be longitudinal or transverse; both types are suitable, provided that the suture of such incisions is always transverse. We prefer a longitudinal incision, because if the retractor on the duodenum widens the duodenotomy, this occurs longitudinally. In the case of a transverse duodenotomy, any inadvertent extension would cause a transverse enlargement of the wound. Identification of the Papilla After the duodenal incision, the papilla is readily shown on the medial duodenal wall in 15% to 20% of patients. When the papilla is not readily visible, it should be detected by displacement and flattening of the mucosal folds. This should be done with great care to avoid tearing of the mucosa, which would hinder good exposure. If this is not the case, digital palpation can be used running the forefinger, introduced through the duodenotomy, across the medial duodenal wall. This maneuver should never be performed with rigid catheters because this may result in the formation of false passages. Sometimes a very small papilla is detected, and its catheterization is difficult or impossible. A Nélaton catheter (4 to 5 Fr) is introduced from the outside or via the cystic duct. Following the line of the catheter-and avoiding plastic catheters, which melt when surgical diathermy is applied-the surgeon makes a cut using surgical diathermy. When a sample for biopsy is required, it should be obtained with a scalpel and be taken only from the outer margin of the incision. Sutures should be placed only on the outer margin of the sphincterotomy to prevent the risk of damage to the duct of Wirsung. The opening of the duct of Wirsung usually is identified as a small orifice from which clear, colorless pancreatic juice flows.
Specifications/Details
These lesions may be of low diabetes classes purchase diabecon 60 caps free shipping, intermediate, or increased signal on T1-weighted images, depending on the protein or hemorrhagic content within the mass, and they are usually hyperintense on T2-weighted sequences. B,T1-weightedout-of-phase image shows low signal at its margin due to chemical shift artifact between the mass and surrounding liver, confirming the presence of bulk fat. Communication with the biliary ductal system on delayed hepatobiliary phase imaging with hepatocyte contrast agents has been reported, helping to differentiate these tumors from nonneoplastic simple hepatic cysts. Infectious cysts may also communicate with the biliary tree, however, such as with complex cysts from echinococcal disease. However, its differentiation from inflammatory conditions, which may occur concurrently, may be difficult (see Chapters 33 and 49). As opposed to the inflammatory associated wall thickening with maintained mucosal and submucosal layers, with differential enhancement, gallbladder cancer typically shows irregular intermediate to high T2 signal thickening of the gallbladder wall, with early and prolonged heterogeneous enhancement, often in patients with multiple gallstones (Tan et al, 2013). Tumors may show focal nodular thickening along ductal walls or be discrete intrahepatic masses. Focused assessment of ductal, portal venous, and hepatic arterial involvement is performed in staging and preoperative imaging. Satellite lesions are common within the liver, and these lesions tend to show low signal intensity on delayed hepatocyte imaging phase (Chung et al, 2009; Kim et al, 2011; Peporte et al, 2013). Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas may show adjacent capsular retraction as well as vascular encasement, typically without tumor thrombus (Chung et al, 2009). Smaller tumors may show early, more uniform arterial enhancement, particularly when less than 4 cm in size (Kim et al, 2011). Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct is an uncommon subtype of bile duct cancer with characteristics similar to pancreatic intraductal mucinous neoplasms. The majority of tumors occur near the hilum or in extrahepatic ducts, and the clinical outcomes are better than conventional bile duct cancers (Rocha et al, 2012). They usually appear as low signal intensity structures in a fluid-filled gallbladder. Choledochal Cysts Choledochal cysts (see Chapter 46) represent dilatation of the extrahepatic bile ducts with possible associated intrahepatic biliary duct dilatation. This entity is a relatively uncommon congenital anomaly that usually presents before 10 years of age. Cysts may be associated with chronic inflammation and increase the risk for cholangiocarcinoma. Recently, there have been advocates for dropping the numeric classification system, instead using a more descriptive, clinically meaningful nomenclature (Visser et al, 2004). A, T1-weighted in-phase gradient-echo image shows a peripheral hypointense mass(m)withcapsularretraction. Imaging characteristics combined with clinical presentation and demographic data often guide therapy and predict the diagnosis. Neoplastic etiologies include tumors arising in the pancreas, such as adenocarcinoma, solid pseudopapillary tumor, neuroendocrine tumors, or pancreatic lymphoma. Metastases, lymphomas, and other rare tumors may involve the pancreas (Low et al, 2011).
Syndromes
- White blood cells, especially lymphocytes, the cells that attack bacteria in the blood
- Slurred speech
- Preschooler development
- Abnormal urine stream
- Fever
- Numbness in the hands, feet, or other areas
- CT scan chest
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: gtt.
Tags: buy diabecon 60 caps without a prescription, cheap diabecon 60 caps online, generic 60 caps diabecon with amex, purchase 60 caps diabecon with visa
9 of 10
Votes: 249 votes
Total customer reviews: 249
Customer Reviews
Temmy, 37 years: Percutaneous treatment of hydatid cysts is associated with a 10% to 11% incidence of biliary fistula (Koroglu et al, 2014; Men et al, 1999). Echinococcal Cysts Hydatid cystic disease is a parasitic disease cause by Echinococcus granulosa (see Chapter 74). The primary nutritional deficit resulting from obstructive jaundice is malabsorption of fat and fatsoluble vitamins.
Bufford, 26 years: Berber E, et al: Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors: prospective clinical evaluation of ablation size comparing two treatment algorithms, Surg Endosc 18(3):390396, 2004. It is important to scan patients in different positions to differentiate gallstones from polyps, because gallstones are mobile, whereas polyps are fixed. These metabolic aberrations lead to altered metabolism of fat, protein, and carbohydrate.
Gunnar, 22 years: The authors did not define inclusion or exclusion criteria, and no definition was provided for "a high-risk" surgical patient. If stone removal from the gallbladder is to be undertaken this should also be performed after tract maturation. Their analysis identified operative procedures exposing the major Glisson capsule and including the hilum- anterior sectorectomy, central hepatectomy, and caudate resections-to be high-risk operations for development of postoperative bile leakage.
Tuwas, 54 years: New dose modulation techniques have also reduced the radiation dose exposure for patients. This difference in signal intensity makes it relatively easy to determine the malignant nature of the lesion but not the specific tumor type. Hence alternative access routes through the remnant stomach directly to the native papilla have been explored.
Julio, 33 years: The region of interest is placed at least 2 cm beneath the anterior capsule to prevent reverberation artifacts, avoiding focal liver lesions and large vessels. Nagai H, et al: Comprehensive allelotyping of human hepatocellular carcinoma, Oncogene 14:29272933, 1997. Embryonic Signaling It is increasingly recognized that embryonic signaling pathways are important in the genesis of numerous types of malignancies.
Hernando, 23 years: Biopsies obtained during endoscopy can assess for dysplasia or unsuspected carcinoma, although malignancy may be missed in up to 30% of tumors when forceps biopsy specimens are obtained (Elek et al, 2003). The test is also valuable in delineating a variety of postcholecystectomy issues beyond retained stones. Decision making is further influenced by clinical presentation, condition of the patient, institutional expertise, and presence or absence of a T-tube.