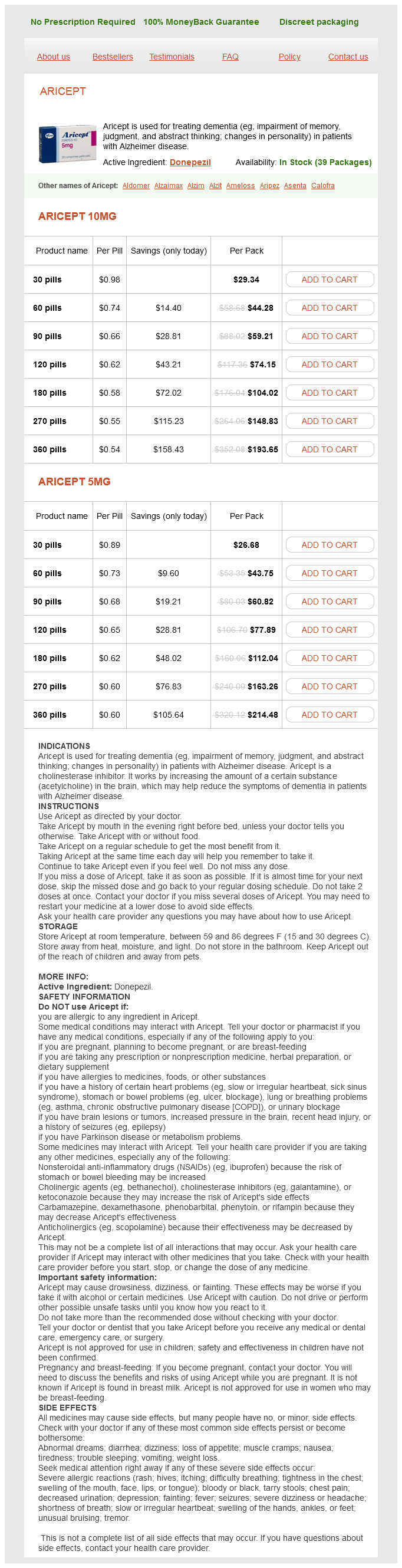
Aricept 10mg
- 30 pills - $29.34
- 60 pills - $44.28
- 90 pills - $59.21
- 120 pills - $74.15
- 180 pills - $104.02
- 270 pills - $148.83
- 360 pills - $193.65
Aricept 5mg
- 30 pills - $26.68
- 60 pills - $43.75
- 90 pills - $60.82
- 120 pills - $77.89
- 180 pills - $112.04
- 270 pills - $163.26
- 360 pills - $214.48
Aricept dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Aricept packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
In stock: 759
Only $0.63 per item
Description
Update on the management and treatment of hepatitis C virus infection: recommendations from the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center Program and the National Hepatitis C Program Office medicine 4839 aricept 10 mg buy otc. Pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability of ribavirin in healthy volunteers as determined by stable-isotope methodology. A multi-drug regimen for respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus infections in adult lung and heart-lung transplant recipients. Placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of intravenous ribavirin for the treatment of hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome in North America. Triple combination of oseltamivir, amantadine, and ribavirin displays synergistic activity against multiple influenza virus strains in vitro. Valaciclovir: a review of its long term utility in the management of genital herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus infections. High-dose acyclovir and pre-emptive ganciclovir in prevention of cytomegalovirus disease in pediatric patients following peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Reischig T, Jindra P, Mares J, Cechura M, Svecova M, Hes O, Opatrny K, Jr, Treska V. Valacyclovir for cytomegalovirus prophylaxis reduces the risk of acute renal allograft rejection. Naesens L, Lenaerts L, Andrei G, Snoeck R, Van Beers D, Holy A, Balzarini J, De Clercq E. Antiadenovirus activities of several classes of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues. Cidofovir for the treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a review of the literature. A review of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in immunocompromised patients with cytomegalovirus retinitis. Pharmacokinetics of intermittently administered intravenous foscarnet in the treatment of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with serious cytomegalovirus retinitis. Immunocompromised hosts: perspectives in the treatment and prophylaxis of cytomegalovirus disease in solid-organ transplant recipients. Valganciclovir results in improved oral absorption of ganciclovir in liver transplant recipients. Pharmacodynamics of oral ganciclovir and valganciclovir in solid organ transplant recipients. Artesunate as a potent antiviral agent in a patient with late drug-resistant cytomegalovirus infection after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Functional studies indicate amantadine binds to the pore of the influenza A virus M2 proton-selective ion channel.
Thea viridis (Black Tea). Aricept.
- Dosing considerations for Black Tea.
- Reducing the risk of hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
- Preventing dizziness upon standing up (orthostatic hypotension) in older people.
- Reducing the risk of kidney stones.
- Reducing the risk of heart attacks.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Osteoporosis, headache, high blood pressure, stomach disorders, vomiting, diarrhea, preventing tooth decay, type 2 diabetes, lung cancer, reducing the risk of cancer, and promoting weight loss.
- Reducing the risk of ovarian cancer.
- What is Black Tea?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96958
Dendritic cells that have taken up antigen migrate through afferent lymphatics to draining lymph nodes or through the blood to the spleen symptoms 4-5 weeks pregnant generic aricept 5 mg buy line. Virgin T cells migrating through the T zones move over the surface of the interdigitating cells and are activated if they meet antigen they recognize. As the result of this priming process, they move to the outer T zone and become targets for B cells that have taken up and processed antigen. B cells activated by these T cells migrate to extrafollicular foci of B-cell proliferation the medullary cords in lymph nodes where they generate short-lived plasma cells. T cells, after a brief period of proliferation in the T zone, either leave the node as effector cells/recirculating memory T cells or migrate to follicles, where they proliferate further and participate in the selection of B cells that have mutated the immunoglobulin variable-region genes in germinal centres. The base of each cone abuts onto the subcapsular lymph sinus in the cortex of the node and the apex is in the medulla. These cones fit together, but are separated by the intranodal lymphatic sinuses, to form the roughly kidney-shaped structure of lymph nodes. The cones have three main zones: the follicles in the cortex, the T zones and the medullary cords. The contents and functions of each of these zones are described in detail in subsequent sections. The 293 Postgraduate Haematology blood supply to the node enters and leaves the node through the medulla, and the specialized small blood vessels termed high endothelial venules are located in the T zones. Virgin B and T cells, and some memory cells, enter the T zone by passing across the high endothelial venules. Cytokines are produced by the T cell following this interaction and the nature of the cytokines produced in different situations is considered later. Short-term proliferation of the T and B cells is also induced, and most B cells migrate to local sites of antibody production. The extent of immunoglobulin class switching will depend on the conditions of dendritic cell activation and T-cell priming. In primary antibody responses, the plasma cells generated by B-cell activation in T zones do not have somatic mutations in their immunoglobulin V-region genes. On the other hand, in secondary responses, marginal-zone memory B cells that have somatic mutations in their V-region genes can be induced to migrate to T zones on contact with antigen and give rise to short-lived plasma cells. The other pathway of migration of T and B cells activated in T zones is to the follicles. Both antigen-specific B blasts and T blasts migrate to the follicles at an early stage in T-zone responses and give rise to germinal centres. At this stage, changes occur whereby the classical germinal centre structures of dark and light zones develop. These blasts, now termed centroblasts, activate the somatic hypermutation mechanism that acts on their rearranged immunoglobulin V-region genes. They can leave the light zone only if they receive antigen-specific selection signals. B cells take up antigen that they bind specifically through their surface immunoglobulin.
Specifications/Details
A number of candidate vaccines have been developed and are in various stages of preclinical and clinical evaluation (for a review treatment quadratus lumborum buy aricept 5 mg, see reference 11). Common disinfectants containing alcohol, detergents, and chlorine are effective in inactivating the virus. The selection of assays to perform and the choice of specimen(s) to be tested depend on the patient population and clinical situation and the intended use of the individual tests. The optimal frequency of blood collection remains to be established for surveillance of different patient groups, although it is common practice to submit blood specimens once a week while monitoring viral loads during preemptive antiviral therapy (9, 10). The first specimen should be collected at the start of therapy to establish a baseline viral load (16). Although peripheral blood leukocytes were commonly used in the past, whole blood and plasma are now considered the specimens of choice (19). A potential limitation for the use of whole blood is the possibility of variation in leukocyte counts from patient to patient; this may lead to erroneous quantitative measurements if fluctuations in cell numbers are not taken into consideration. When monitoring patients over time, the same specimen type should be used to minimize the variations observed between different blood compartments. The blood should be kept at 4°C during storage and transport and should be processed within 6 to 8 h of collection for accurate and reliable quantitation of the viral load and within 24 h and no later than 48 h for qualitative testing (21). A decrease in quantitative antigenemia levels after storage of blood specimens for 24 h to 48 h has been described, although most positive specimens remain positive after this time when held at 4°C (21, 22). As a general rule, specimens for molecular amplification should be stored at 4°C immediately after collection and then promptly transported to the laboratory for processing. Single-use aliquots of processed specimens should be placed in multiple cryovials for testing and storage. If not tested immediately, specimens should be promptly frozen and stored at -70°C. Impression smears, frozen sections, or formaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded material can be used for in situ hybridization or histopathologic examination of tissue specimens obtained from patients with pneumonia, gastrointestinal disease, hepatitis, myocarditis, retinitis, pancreatitis, nephritis, cystitis, or central nervous system disease. Amniotic fluid should be collected after 21 to 23 weeks of fetal gestation for best sensitivity (25). However, dried blood spots and blood in general are not as sensitive as urine or saliva for newborn screening. All tissue specimens should be placed in a suitable viral transport medium immediately after collection. When prolonged transport times are unavoidable, infectivity is reasonably well preserved for at least 48 h at 4°C. This approach is especially helpful in testing sera from organ transplant donors and recipients before transplantation and from donors of blood products that are to be administered to premature infants or bone marrow transplant patients. The acute-phase serum sample should be collected as soon as possible after onset of illness and tested simultaneously with the convalescentphase serum sample. When testing for IgM in the fetus, blood should be collected after 22 weeks of gestation since fetal synthesis of antibodies starts at 20 weeks of gestation and may not reach detectable levels for 1 to 2 more weeks.
Syndromes
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Phenazopyridine
- Injury to the nail
- Acne that is deep in your skin can cause hard, painful cysts. This is called cystic acne.
- Chronic urinary tract infections
- Take the drugs your doctor told you to take with a small sip of water.
- Amphetamines
Related Products
Additional information:
Usage: q.h.
Tags: generic 5 mg aricept with mastercard, 5 mg aricept purchase with visa, 10 mg aricept order mastercard, order 5 mg aricept fast delivery
8 of 10
Votes: 274 votes
Total customer reviews: 274
Customer Reviews
Ballock, 56 years: Continued observation is necessary due to late relapses and large-cell transformation (typically to T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma). The integral proteins have strong hydrophobic domains that associate with the hydrophobic part of the bilayer. The gender gap in iron deficiency anaemia has widened in recent years on a worldwide basis. However, it is now clear that the disorder is not just limited to the Mediterranean region, but occurs throughout the world, prevalent in the tropical and subtropical regions, including the Middle East, parts of Africa, Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
Tufail, 59 years: If the antibody screening is positive, antibody identification against a panel of 812 fully phenotyped red cells should be performed. Total collectomy with ileorectal colic artery and the right branch of midanastomosis. Homozygosity for pC282Y is more frequent in patients with cirrhosis and hepatoma than in the general population. Intestinal amebiasis/giardiasis or other worm infestations may mimic acute abdomen.